Contributions
Abstract: S1588
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Sunday, June 17, 2018 from 08:45 - 09:00
Location: Room A9
Background
Patients with SCA are at significantly increased risk of cerebrovascular disease (CVD). The role of genetics in the pathogenesis of CVD is supported by analysis of sibling pairs in both stroke outcomes and cerebrovasculopathy as detected by abnormal transcranial Doppler (TCD) studies. Another form of CVD in SCA are silent cerebral infarcts (SCI). These do not cause overt clinical signs, but are associated with reduction in IQ.
Aims
To perform genome wide association analysis of CVD outcomes in patients with SCA.
Methods
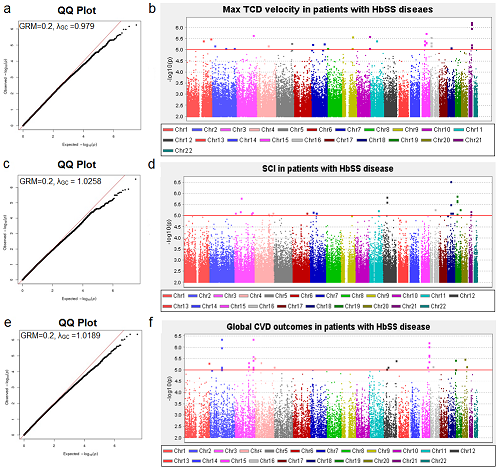
The south east London sickle cell disease genebank contains 832 African-Caribbean or West African heritage patients with datasets for 16.7 million non-monomorphic variants based on the Illumina Infinium MEGA chip plus imputation using the Michigan imputation server with 1000 genomes data. All available clinical neuroimaging reports (CT scans, MRI/A scans and TCDs) were reviewed to determine evidence of overt ischemic stroke (OIS), SCI and the highest TCD velocity recorded. Clinical notes were also reviewed to confirm OIS. We performed GWAS on OIS, SCI, max TCD, and a fourth composite “global” CVD outcome. Analysis used linear mixed modelling to account for genetic relatedness, with age and sex as fixed covariates. Duplicate samples, and one of a pair of genetically identified 1st or 2nd degree relatives, were removed. Each model was assessed with λGC and a QQ plot to evaluate genomic inflation.
Results
Although no variants achieved genome wide statistical significance, we investigated the most promising variant clusters seen on each Manhattan plot. A GWAS for TCD velocities was performed on 167 patients. The most significant peak was on chromosome 21 (rs2898354, Mean Allele Frequency (MAF)=0.43, p=5.69e-07). These variants sit within intron 4 of the ERG gene, which has previously been associated with stroke in SCA. A cluster was also found on chromosome 9 (rs75829124, MAF=0.03, p=8.53e-06) within 40kB of the TGFBR1 gene. TGFBR3 has previously been associated with stroke in SCA, and TGFBR1 may have a role in the same pathway. A cluster (rs8032902, MAF=0.2, p=4.02e-06) on chromosome 15 sits 40kB upstream of fibrillin 1, the major constitutive element of extracellular microfibrils in blood vessels.
A GWAS for the SCI outcome was performed on 292 patients. The most promising cluster (rs879261, MAF=0.5, p=6.53e-06) sits on chromosome 21 within intron 28 of the intersectin1 gene. Intersectin1 is involved in the endocytosis of Integrin beta-1 and transferrin.
The GWAS model for OIS (n=317) showed evidence of genomic inflation. Modelling difficulties were likely due to the small number of patients with a positive event. Further analysis will be considered when more patients are recruited.
A GWAS for global CVD was performed on 365 patients. A cluster of variants (rs150417193, MAF=0.2, p=7.47e-06) on chromosome 15, sit within a copy number variant affecting a transcription factor binding site ~15kB upstream of ADAMTS7. The ADAMTS family have shown association with pediatric stroke and cardiovascular traits in the general population.
Conclusion
This is one of the largest studies looking at the genetics of CVD in SCD. We performed GWAS on a number of cerebrovascular outcomes in SCA. Although no result achieved genome-wide statistical significance, we have identified areas worthy of further validation. The most significant finding is a cluster of variants that fall within ERG, an erythroblast transformation-specific transcription factor that has a role in vascular cell remodelling, supporting previously published associations with this gene and CVD in SCA.
Session topic: 27. Sickle cell disease
Keyword(s): Cerebrovascular disease, Genomics, Sickle cell anemia
Abstract: S1588
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Sunday, June 17, 2018 from 08:45 - 09:00
Location: Room A9
Background
Patients with SCA are at significantly increased risk of cerebrovascular disease (CVD). The role of genetics in the pathogenesis of CVD is supported by analysis of sibling pairs in both stroke outcomes and cerebrovasculopathy as detected by abnormal transcranial Doppler (TCD) studies. Another form of CVD in SCA are silent cerebral infarcts (SCI). These do not cause overt clinical signs, but are associated with reduction in IQ.
Aims
To perform genome wide association analysis of CVD outcomes in patients with SCA.
Methods
The south east London sickle cell disease genebank contains 832 African-Caribbean or West African heritage patients with datasets for 16.7 million non-monomorphic variants based on the Illumina Infinium MEGA chip plus imputation using the Michigan imputation server with 1000 genomes data. All available clinical neuroimaging reports (CT scans, MRI/A scans and TCDs) were reviewed to determine evidence of overt ischemic stroke (OIS), SCI and the highest TCD velocity recorded. Clinical notes were also reviewed to confirm OIS. We performed GWAS on OIS, SCI, max TCD, and a fourth composite “global” CVD outcome. Analysis used linear mixed modelling to account for genetic relatedness, with age and sex as fixed covariates. Duplicate samples, and one of a pair of genetically identified 1st or 2nd degree relatives, were removed. Each model was assessed with λGC and a QQ plot to evaluate genomic inflation.
Results
Although no variants achieved genome wide statistical significance, we investigated the most promising variant clusters seen on each Manhattan plot. A GWAS for TCD velocities was performed on 167 patients. The most significant peak was on chromosome 21 (rs2898354, Mean Allele Frequency (MAF)=0.43, p=5.69e-07). These variants sit within intron 4 of the ERG gene, which has previously been associated with stroke in SCA. A cluster was also found on chromosome 9 (rs75829124, MAF=0.03, p=8.53e-06) within 40kB of the TGFBR1 gene. TGFBR3 has previously been associated with stroke in SCA, and TGFBR1 may have a role in the same pathway. A cluster (rs8032902, MAF=0.2, p=4.02e-06) on chromosome 15 sits 40kB upstream of fibrillin 1, the major constitutive element of extracellular microfibrils in blood vessels.
A GWAS for the SCI outcome was performed on 292 patients. The most promising cluster (rs879261, MAF=0.5, p=6.53e-06) sits on chromosome 21 within intron 28 of the intersectin1 gene. Intersectin1 is involved in the endocytosis of Integrin beta-1 and transferrin.
The GWAS model for OIS (n=317) showed evidence of genomic inflation. Modelling difficulties were likely due to the small number of patients with a positive event. Further analysis will be considered when more patients are recruited.
A GWAS for global CVD was performed on 365 patients. A cluster of variants (rs150417193, MAF=0.2, p=7.47e-06) on chromosome 15, sit within a copy number variant affecting a transcription factor binding site ~15kB upstream of ADAMTS7. The ADAMTS family have shown association with pediatric stroke and cardiovascular traits in the general population.

Conclusion
This is one of the largest studies looking at the genetics of CVD in SCD. We performed GWAS on a number of cerebrovascular outcomes in SCA. Although no result achieved genome-wide statistical significance, we have identified areas worthy of further validation. The most significant finding is a cluster of variants that fall within ERG, an erythroblast transformation-specific transcription factor that has a role in vascular cell remodelling, supporting previously published associations with this gene and CVD in SCA.
Session topic: 27. Sickle cell disease
Keyword(s): Cerebrovascular disease, Genomics, Sickle cell anemia