Contributions
Abstract: S1577
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Sunday, June 17, 2018 from 08:30 - 08:45
Location: Room A7
Background
Daratumumab (DARA) is a human monoclonal IgG1κ CD38-targeted antibody that has several mechanisms of action, including complement-dependent cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis, modulation of CD38 enzymatic activity, and induction of apoptosis with antibody cross-linking. DARA (16 mg/kg) single-agent, phase 1/2 translational studies (SIRIUS and GEN501) revealed an additional, novel immunomodulatory mechanism of action that increased the adaptive immune response in multiple myeloma (MM). Natural killer (NK) cells were reduced in these studies, with no effect on DARA efficacy or safety (Casneuf T et al, Blood Adv. 2017;1[23]:2105-2114; Adams HC 3rd et al, Presented at ASH 2016; Abstract 4521). Furthermore, subsequent combination studies showed DARA promotes robust pro-adaptive immunological changes when combined with lenalidomide and dexamethasone (van de Donk NWCJ et al, Presented at ASH 2017; Abstract 3124).
Aims
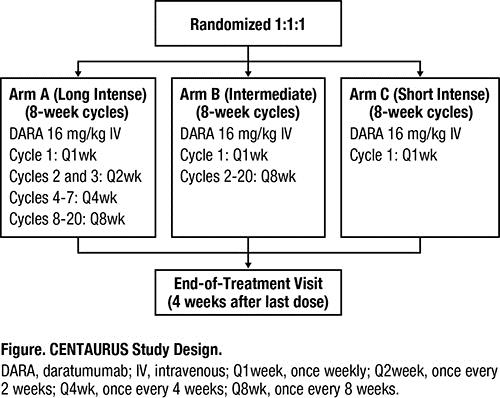
To explore the ability of DARA to promote adaptive T-cell responses and immune changes in asymptomatic SMM patients (pts) in CENTAURUS (Figure; NCT02316106) using cytometry by time-of-flight (CyTOF®).
Methods
Intermediate and high-risk SMM pt whole-blood samples from three treatment arms were analyzed: Long (L), Intermediate (I) and Short (S) at Cycle 1 Day 1 (L, n=34; I, n=39; S, n=30) and after a minimum of one cycle of DARA (16 mg/kg intravenous) monotherapy (L at Cycle 4 Day 1, n=33; I at Cycle 4 Day 1, n=36; S at End of Treatment, n=30). Samples were stained with a metal-conjugated antibody panel and evaluated by CyTOF®. Similar cellular events were clustered into nodes using the spanning tree progression of density normalized events (SPADE) algorithm and annotated into immune-cell populations via Cytobank® software. Differences in marker intensity and cell populations within subgroups were defined by P values derived from Student T-tests over time and at baseline. Results were visualized by SPADE-blend trees, where each cluster was colored using a combination of P values related to marker intensity and cell-population size changes, and using Radviz projections to monitor complex effects.
Results
Consistent with previous studies, we observed a reduction in circulating NK cells, along with CD38 downregulation predominantly in NK cells, basophils, and CD38+ regulatory T cells (CD3+CD4+CD25+CD127–), in all treatment arms. The proportion of T cells increased across all arms and was correlated with a higher proportion of CD8+ versus CD4+ T cells. After DARA administration, the total T-cell populations shifted towards CD8+ T cells with increased production of granzyme B, a cytolytic enzyme. Prominent increases in the CD8+ T-cell effector memory compartment were observed in post-DARA/on-study samples. Likely driven by differences in time of collection between treatment arms, the increase in expression of the activation marker HLA-DR was more pronounced in CD8+ central memory and effector memory T cells of pts in the S arm, while granzyme B increased independent of treatment arm.
Conclusion
DARA administration across the three treatment arms induced clinical responses in pts and T-cell profile changes, including expansion of effector memory T cells and increased expression of activation markers. These changes are conducive to adaptive immunity. As SMM pts are relatively more immune-competent compared to MM pts, this study again demonstrates DARA’s immunomodulatory activity in asymptomatic SMM which may play a part in delaying the progression to MM.
Session topic: 13. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): immunomodulation, Multiple Myeloma, Smoldering
Abstract: S1577
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Sunday, June 17, 2018 from 08:30 - 08:45
Location: Room A7
Background
Daratumumab (DARA) is a human monoclonal IgG1κ CD38-targeted antibody that has several mechanisms of action, including complement-dependent cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis, modulation of CD38 enzymatic activity, and induction of apoptosis with antibody cross-linking. DARA (16 mg/kg) single-agent, phase 1/2 translational studies (SIRIUS and GEN501) revealed an additional, novel immunomodulatory mechanism of action that increased the adaptive immune response in multiple myeloma (MM). Natural killer (NK) cells were reduced in these studies, with no effect on DARA efficacy or safety (Casneuf T et al, Blood Adv. 2017;1[23]:2105-2114; Adams HC 3rd et al, Presented at ASH 2016; Abstract 4521). Furthermore, subsequent combination studies showed DARA promotes robust pro-adaptive immunological changes when combined with lenalidomide and dexamethasone (van de Donk NWCJ et al, Presented at ASH 2017; Abstract 3124).
Aims
To explore the ability of DARA to promote adaptive T-cell responses and immune changes in asymptomatic SMM patients (pts) in CENTAURUS (Figure; NCT02316106) using cytometry by time-of-flight (CyTOF®).
Methods
Intermediate and high-risk SMM pt whole-blood samples from three treatment arms were analyzed: Long (L), Intermediate (I) and Short (S) at Cycle 1 Day 1 (L, n=34; I, n=39; S, n=30) and after a minimum of one cycle of DARA (16 mg/kg intravenous) monotherapy (L at Cycle 4 Day 1, n=33; I at Cycle 4 Day 1, n=36; S at End of Treatment, n=30). Samples were stained with a metal-conjugated antibody panel and evaluated by CyTOF®. Similar cellular events were clustered into nodes using the spanning tree progression of density normalized events (SPADE) algorithm and annotated into immune-cell populations via Cytobank® software. Differences in marker intensity and cell populations within subgroups were defined by P values derived from Student T-tests over time and at baseline. Results were visualized by SPADE-blend trees, where each cluster was colored using a combination of P values related to marker intensity and cell-population size changes, and using Radviz projections to monitor complex effects.
Results
Consistent with previous studies, we observed a reduction in circulating NK cells, along with CD38 downregulation predominantly in NK cells, basophils, and CD38+ regulatory T cells (CD3+CD4+CD25+CD127–), in all treatment arms. The proportion of T cells increased across all arms and was correlated with a higher proportion of CD8+ versus CD4+ T cells. After DARA administration, the total T-cell populations shifted towards CD8+ T cells with increased production of granzyme B, a cytolytic enzyme. Prominent increases in the CD8+ T-cell effector memory compartment were observed in post-DARA/on-study samples. Likely driven by differences in time of collection between treatment arms, the increase in expression of the activation marker HLA-DR was more pronounced in CD8+ central memory and effector memory T cells of pts in the S arm, while granzyme B increased independent of treatment arm.

Conclusion
DARA administration across the three treatment arms induced clinical responses in pts and T-cell profile changes, including expansion of effector memory T cells and increased expression of activation markers. These changes are conducive to adaptive immunity. As SMM pts are relatively more immune-competent compared to MM pts, this study again demonstrates DARA’s immunomodulatory activity in asymptomatic SMM which may play a part in delaying the progression to MM.
Session topic: 13. Myeloma and other monoclonal gammopathies – Biology & Translational Research
Keyword(s): immunomodulation, Multiple Myeloma, Smoldering