Contributions
Abstract: S805
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Saturday, June 16, 2018 from 11:45 - 12:00
Location: Victoria Hall
Background
Improved survival outcomes with chemoimmunotherapy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are associated with minimal residual disease negativity (MRD–; <1 CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes [<10 -4]), but the importance of MRD with targeted agents and in the relapsed/refractory (R/R) setting remains unclear, mostly due to low MRD– rates with these agents. In the Phase 3 MURANO study, venetoclax + rituximab (VenR) showed superior PFS (hazard ratio 0.17) and higher peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) MRD– vs bendamustine + R (BR) in R/R CLL patients.
Aims
To report MRD kinetics (percent of patients achieving MRD <10-4, 10-4 to <10-2, and ≥10-2, at various timepoints), and MRD response in CLL cytogenetic and molecular risk groups in patients from MURANO.
Methods
Patients were randomized to VenR for 6 months followed by single-agent Ven ≤1.5 years, or to BR for 6 months. PB samples were serially collected whereas BM samples were collected at the end of combination treatment assessment (EOCT; Month 9) or at best response; MRD was analyzed centrally by ASO-PCR and/or flow cytometry.
Results
High concordance was observed between PB and BM MRD status (84%) in patients with paired samples. Higher agreement in MRD– between BM and PB was seen with VenR (45/50 [90%] PB MRD– were also BM MRD–) compared with BR (3/10 [30%]). Given this concordance and availability of serial PB sampling, we focus on PB MRD and outcome.
Best MRD– (at any time on study) rates were higher with VenR (84% vs 23% in BR), and were independent of high-risk cytogenetic and molecular factors only for VenR: del(17p) present vs absent: 83% vs 87%; TP53 mutated vs unmutated: 73% vs 88%; IGVH unmutated vs mutated: 82% vs 89%.
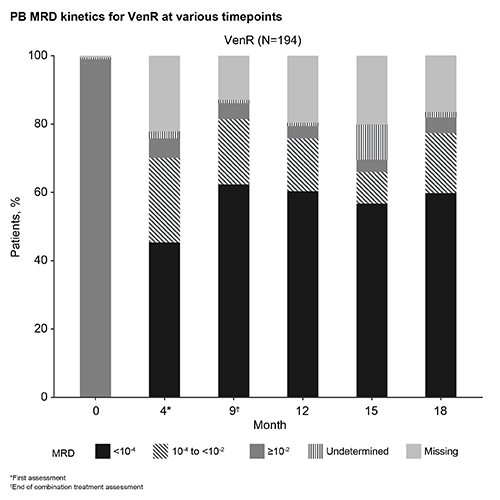
PB MRD kinetics for VenR are shown in the Figure. Among 121/194 (62%) patients who were MRD– at EOCT with VenR: 100 (83%) maintained MRD– and were PFS free at a median follow-up of 13.8 (5.6–23.0) months; 2 patients developed progressive disease (PD); 2 died (unrelated); and 2 patients developed Richter’s syndrome (with one MRD+ directly before). The remaining 15/121 (12%) patients converted to confirmed MRD+ (2 serial assay-positive assessments) at a median MRD+ follow-up of 5.6 (0.03–11.2) months; 1 patient had MRD ≥10-2 with PD, 14 patients had MRD 10-4 to <10-2, 2 of which had PD, 1 patient died, and 11 patients remained PFS free. MRD kinetics by patient including treatment status will be presented.
Conclusion
The robust PB MRD and high concordance with BM MRD with VenR confirms the value of PB MRD for correlation with clinical outcome in patients with R/R CLL treated with this regimen. VenR achieves high, early, deep and durable PB MRD– regardless of risk features, unlike BR. Some reemergence of MRD+, mainly intermediate (10-4 to <10-2) level, is seen only in a small number of patients, and may not lead to clinical PD, consistent with the PFS benefit observed in the MURANO study. NCT02005471
Session topic: 6. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Minimal residual disease (MRD), Phase III, Targeted therapy
Abstract: S805
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA23: On Saturday, June 16, 2018 from 11:45 - 12:00
Location: Victoria Hall
Background
Improved survival outcomes with chemoimmunotherapy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) are associated with minimal residual disease negativity (MRD–; <1 CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes [<10 -4]), but the importance of MRD with targeted agents and in the relapsed/refractory (R/R) setting remains unclear, mostly due to low MRD– rates with these agents. In the Phase 3 MURANO study, venetoclax + rituximab (VenR) showed superior PFS (hazard ratio 0.17) and higher peripheral blood (PB) and bone marrow (BM) MRD– vs bendamustine + R (BR) in R/R CLL patients.
Aims
To report MRD kinetics (percent of patients achieving MRD <10-4, 10-4 to <10-2, and ≥10-2, at various timepoints), and MRD response in CLL cytogenetic and molecular risk groups in patients from MURANO.
Methods
Patients were randomized to VenR for 6 months followed by single-agent Ven ≤1.5 years, or to BR for 6 months. PB samples were serially collected whereas BM samples were collected at the end of combination treatment assessment (EOCT; Month 9) or at best response; MRD was analyzed centrally by ASO-PCR and/or flow cytometry.
Results
High concordance was observed between PB and BM MRD status (84%) in patients with paired samples. Higher agreement in MRD– between BM and PB was seen with VenR (45/50 [90%] PB MRD– were also BM MRD–) compared with BR (3/10 [30%]). Given this concordance and availability of serial PB sampling, we focus on PB MRD and outcome.
Best MRD– (at any time on study) rates were higher with VenR (84% vs 23% in BR), and were independent of high-risk cytogenetic and molecular factors only for VenR: del(17p) present vs absent: 83% vs 87%; TP53 mutated vs unmutated: 73% vs 88%; IGVH unmutated vs mutated: 82% vs 89%.
PB MRD kinetics for VenR are shown in the Figure. Among 121/194 (62%) patients who were MRD– at EOCT with VenR: 100 (83%) maintained MRD– and were PFS free at a median follow-up of 13.8 (5.6–23.0) months; 2 patients developed progressive disease (PD); 2 died (unrelated); and 2 patients developed Richter’s syndrome (with one MRD+ directly before). The remaining 15/121 (12%) patients converted to confirmed MRD+ (2 serial assay-positive assessments) at a median MRD+ follow-up of 5.6 (0.03–11.2) months; 1 patient had MRD ≥10-2 with PD, 14 patients had MRD 10-4 to <10-2, 2 of which had PD, 1 patient died, and 11 patients remained PFS free. MRD kinetics by patient including treatment status will be presented.

Conclusion
The robust PB MRD and high concordance with BM MRD with VenR confirms the value of PB MRD for correlation with clinical outcome in patients with R/R CLL treated with this regimen. VenR achieves high, early, deep and durable PB MRD– regardless of risk features, unlike BR. Some reemergence of MRD+, mainly intermediate (10-4 to <10-2) level, is seen only in a small number of patients, and may not lead to clinical PD, consistent with the PFS benefit observed in the MURANO study. NCT02005471
Session topic: 6. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia and related disorders - Clinical
Keyword(s): Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia, Minimal residual disease (MRD), Phase III, Targeted therapy