Contributions
Abstract: PB2218
Type: Publication Only
Background
The calibrated automated thrombogram (CAT) is a method to monitor the generation of thrombin. It can be described by four variables; lag time, peak thrombin, time to peak, and velocity index. Currently, due to thromboembolic event related risks of immunoglobulins, the CAT is widely used to quantify the thrombogenic potential associated with immunoglobulin manufacturing processes and products. However, there is currently no officially approved method for such assessments and even this results are highly variable in inter-laboratories comparison. In this study, to obtain a summary score, we applied the principal component analysis (PCA) for these four outcomes measured from CAT method. The PCA is a statistical procedure concerned with elucidating the covariance structure of a set of variables. In particular it allows us to identify the principal directions in which the data varies.
Aims
In this study, our interest is to apply PCA method in order to find appropriate dose related with CAT variables and to reduce variation of procoagulant values in Immunoglobulin products.
Methods
The CAT are measured in a 96 well plate fluorometer equipped with a 390/460 filter set and a dispenser. Usually experiments are carried out in triplicate. During the measurement, a dedicated software program, Thrombinoscope compares the readings from the trigger wells and the calibrater wells, calculates thrombin concentration and displays the thrombin concentration in time. Outcomes from CAT were analyzed in the principal component anaysis (PCA) which is a statistical procedure that allows us to summarize high dimensional data with a smaller number of representative variables that collectively explain most of the variability. Statistical analyses were performed with R 2.5.
Results
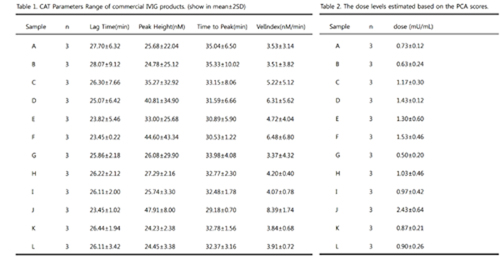
Four variables measured from CAT have different sistribution and too large variations. For example, the mean(sd) of each variable (lag time, peak thrombin, time to peak, and velocity index) are 24.66(8.01), 80.16(94.52), 31.28(9.78), 19.08(28.86), respectively. Therefore, to remedy such high variability among variables and to find a score, PCA method is applied. Then the dose values calculated based on the PCA scores have mean 0.393 and a much smaller variation (sd = 0.583).
Conclusion
The PCA value showed a good agreement with four CAT outcomes and less variation. The PCA method could be used to monitor the process of immunoglobulin manufacturing.
Session topic: 34. Thrombosis and vascular biology
Keyword(s): Thrombin generation, Procoagulant, Immunoglobulin
Abstract: PB2218
Type: Publication Only
Background
The calibrated automated thrombogram (CAT) is a method to monitor the generation of thrombin. It can be described by four variables; lag time, peak thrombin, time to peak, and velocity index. Currently, due to thromboembolic event related risks of immunoglobulins, the CAT is widely used to quantify the thrombogenic potential associated with immunoglobulin manufacturing processes and products. However, there is currently no officially approved method for such assessments and even this results are highly variable in inter-laboratories comparison. In this study, to obtain a summary score, we applied the principal component analysis (PCA) for these four outcomes measured from CAT method. The PCA is a statistical procedure concerned with elucidating the covariance structure of a set of variables. In particular it allows us to identify the principal directions in which the data varies.
Aims
In this study, our interest is to apply PCA method in order to find appropriate dose related with CAT variables and to reduce variation of procoagulant values in Immunoglobulin products.
Methods
The CAT are measured in a 96 well plate fluorometer equipped with a 390/460 filter set and a dispenser. Usually experiments are carried out in triplicate. During the measurement, a dedicated software program, Thrombinoscope compares the readings from the trigger wells and the calibrater wells, calculates thrombin concentration and displays the thrombin concentration in time. Outcomes from CAT were analyzed in the principal component anaysis (PCA) which is a statistical procedure that allows us to summarize high dimensional data with a smaller number of representative variables that collectively explain most of the variability. Statistical analyses were performed with R 2.5.
Results
Four variables measured from CAT have different sistribution and too large variations. For example, the mean(sd) of each variable (lag time, peak thrombin, time to peak, and velocity index) are 24.66(8.01), 80.16(94.52), 31.28(9.78), 19.08(28.86), respectively. Therefore, to remedy such high variability among variables and to find a score, PCA method is applied. Then the dose values calculated based on the PCA scores have mean 0.393 and a much smaller variation (sd = 0.583).

Conclusion
The PCA value showed a good agreement with four CAT outcomes and less variation. The PCA method could be used to monitor the process of immunoglobulin manufacturing.
Session topic: 34. Thrombosis and vascular biology
Keyword(s): Thrombin generation, Procoagulant, Immunoglobulin