Contributions
Abstract: S794
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Sunday, June 25, 2017 from 08:00 - 08:15
Location: Room N105
Background
Aims
Here, we present 21-marker FACS analysis of blood from patients enrolled in a prospective, randomized, parallel-cohort, open-label phase 1 trial of the potent and selective JAK1 inhibitor INCB039110 for aGVHD (NCT02614612). Preliminary results were previously presented at ASH 2016 (Schroeder et al).
Methods
Patients (n=30) were >18 years old undergoing first alloHSCT from any source with steroid-refractory or treatment-naïve grades IIB-IVD aGVHD, randomized 1:1 to 200 or 300 mg oral daily INCB039110 combined with corticosteroids. Peripheral blood, obtained at treatment days 7, 14, 28, 56, 100, and 180, was analyzed by 21-color FACS quantifying >30 cell types, including B, CD4+ and CD8+ T, memory T, T regulatory (Treg), Th1, Th2, Th17, T follicular helper (Tfh), Th9, Th22, ThGM-CSF cells, granulocytes, monocytes, monocyte-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), natural killer cells (NKs), and monocytic and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs). Patients were stratified by treatment response (e.g. complete response (CR), partial response (PR), mixed response (MR)).
Results
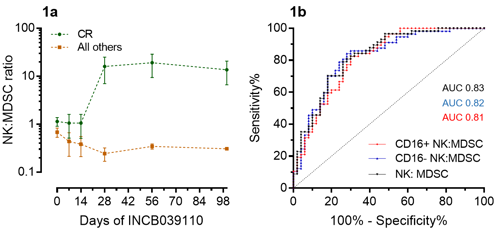
During INCB039110 treatment, overall B, T, and myeloid proportions did not correlate with response. However, the CR group showed increased NK cells (CD3-CD20-CD14-HLADR-CD56+), mDCs (CD3-CD20-CD14-HLADR+CD11c+), and memory CD4+ T cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RA-). Among CD4+ memory cells, the CR group showed significant or trend-toward-significant increases in Tfh (CCR10-CXCR5+), Th1 (CXCR5-CCR6-CCR10-CXCR3+), Th2, Th17 (CXCR5-CCR6+CCR4+CXCR3-CCR10-), ThGM-CSF (CXCR5-CCR6-CCR10+CXCR3-), and Th22 (CXCR5-CCR6+CCR4+CXCR3-CCR10+) cells. Tregs (CD4+CD25+CD127-) trended toward a ~2-fold increase in the CR group. Within the monocyte subgroup (CD3-CD20-CD14+), the CR group skewed toward classical monocytes (HLADR+CD16-) (64.7% vs 36.0%, CR vs. PR/MR, p=0.0078) and away from MDSCs (HLADR-CD16-) (30.0% vs. 58.4%, CR vs. PR/MR, p=0.0139) during treatment. Interestingly, the NK-to-MDSC ratio was a sensitive and specific predictor of CR vs. all other responses, a finding consistent for both CD16+ and CD16- NK cells (Figures 1a-b). Before treatment, decreased naïve CD8+ T cells (CD45RA+CCR7+) predicted CR versus PR/MR (12.6% vs. 32.3% of CD8+ cells, CR vs. PR/MR, p=0.0047) with a similar trend toward decreased naïve CD4+ T cells (13% vs. 24.4% of CD4+ cells, CR vs PR/MR, p=0.0749). While naïve T cells did not correlate with pre-treatment aGVHD grade, grades III-IV aGVHD demonstrated increased Th2 cells (CD45RA-CXCR5-CCR6-CCR10-CXCR3-) and activated CD8+ cells (CD38+HLADR+) as compared to grade II aGVHD. Further correlation with serum cytokines, JAK-STAT signaling, and pharmacology will be available at time of presentation.
Conclusion
Decreased pre-treatment naïve T cells may predict better outcomes in INCB039110-treated aGVHD. During treatment, increased DCs, NKs, and memory T cell subsets correlated with better response. Surprisingly, increased MDSCs associated with poorer response, suggesting MDSC expansion during persistent inflammation. The NK-to-MDSC ratio may be an important clinical marker to track treatment progress. Finally, this study establishes a novel FACS-based 21-marker immunophenotyping method with superior throughput, sample preservation, and flexibility as compared to cytometry time of flight (CyTOF) methods.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Janus Kinase inhibitor, Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), flow cytometry, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Abstract: S794
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA22: On Sunday, June 25, 2017 from 08:00 - 08:15
Location: Room N105
Background
Aims
Here, we present 21-marker FACS analysis of blood from patients enrolled in a prospective, randomized, parallel-cohort, open-label phase 1 trial of the potent and selective JAK1 inhibitor INCB039110 for aGVHD (NCT02614612). Preliminary results were previously presented at ASH 2016 (Schroeder et al).
Methods
Patients (n=30) were >18 years old undergoing first alloHSCT from any source with steroid-refractory or treatment-naïve grades IIB-IVD aGVHD, randomized 1:1 to 200 or 300 mg oral daily INCB039110 combined with corticosteroids. Peripheral blood, obtained at treatment days 7, 14, 28, 56, 100, and 180, was analyzed by 21-color FACS quantifying >30 cell types, including B, CD4+ and CD8+ T, memory T, T regulatory (Treg), Th1, Th2, Th17, T follicular helper (Tfh), Th9, Th22, ThGM-CSF cells, granulocytes, monocytes, monocyte-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), natural killer cells (NKs), and monocytic and plasmacytoid dendritic cells (DCs). Patients were stratified by treatment response (e.g. complete response (CR), partial response (PR), mixed response (MR)).
Results
During INCB039110 treatment, overall B, T, and myeloid proportions did not correlate with response. However, the CR group showed increased NK cells (CD3-CD20-CD14-HLADR-CD56+), mDCs (CD3-CD20-CD14-HLADR+CD11c+), and memory CD4+ T cells (CD3+CD4+CD45RA-). Among CD4+ memory cells, the CR group showed significant or trend-toward-significant increases in Tfh (CCR10-CXCR5+), Th1 (CXCR5-CCR6-CCR10-CXCR3+), Th2, Th17 (CXCR5-CCR6+CCR4+CXCR3-CCR10-), ThGM-CSF (CXCR5-CCR6-CCR10+CXCR3-), and Th22 (CXCR5-CCR6+CCR4+CXCR3-CCR10+) cells. Tregs (CD4+CD25+CD127-) trended toward a ~2-fold increase in the CR group. Within the monocyte subgroup (CD3-CD20-CD14+), the CR group skewed toward classical monocytes (HLADR+CD16-) (64.7% vs 36.0%, CR vs. PR/MR, p=0.0078) and away from MDSCs (HLADR-CD16-) (30.0% vs. 58.4%, CR vs. PR/MR, p=0.0139) during treatment. Interestingly, the NK-to-MDSC ratio was a sensitive and specific predictor of CR vs. all other responses, a finding consistent for both CD16+ and CD16- NK cells (Figures 1a-b). Before treatment, decreased naïve CD8+ T cells (CD45RA+CCR7+) predicted CR versus PR/MR (12.6% vs. 32.3% of CD8+ cells, CR vs. PR/MR, p=0.0047) with a similar trend toward decreased naïve CD4+ T cells (13% vs. 24.4% of CD4+ cells, CR vs PR/MR, p=0.0749). While naïve T cells did not correlate with pre-treatment aGVHD grade, grades III-IV aGVHD demonstrated increased Th2 cells (CD45RA-CXCR5-CCR6-CCR10-CXCR3-) and activated CD8+ cells (CD38+HLADR+) as compared to grade II aGVHD. Further correlation with serum cytokines, JAK-STAT signaling, and pharmacology will be available at time of presentation.

Conclusion
Decreased pre-treatment naïve T cells may predict better outcomes in INCB039110-treated aGVHD. During treatment, increased DCs, NKs, and memory T cell subsets correlated with better response. Surprisingly, increased MDSCs associated with poorer response, suggesting MDSC expansion during persistent inflammation. The NK-to-MDSC ratio may be an important clinical marker to track treatment progress. Finally, this study establishes a novel FACS-based 21-marker immunophenotyping method with superior throughput, sample preservation, and flexibility as compared to cytometry time of flight (CyTOF) methods.
Session topic: 22. Stem cell transplantation - Clinical
Keyword(s): Janus Kinase inhibitor, Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), flow cytometry, Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant