Contributions
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 14.06.2015 08:45 to 14.06.2015 09:00
Location: Room Lehar 3 + 4
Background
The PD-1 pathway functions as a checkpoint which limits T-cell mediated tumor immune responses. Nivolumab (NIVO), a fully human IgG4 monoclonal PD-1 blocking antibody, potentiates T-cell activity. Prior results from this study (median follow-up 40 weeks) showed that NIVO was tolerated and achieved an overall response rate of 87% in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), 40% in follicular B-cell lymphoma (FBL), 36% in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 17% in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (T-NHL). The stable disease rate in multiple myeloma (MM) was 67%.
Aims
Herein, we report the updated follow-up and safety profile of this study.
Methods
Patients (Pts) were treated using a dose-escalation design (1 and 3 mg/kg) of NIVO administered every 2 weeks (wks) for 2 years. Responses were assessed using standard criteria. Primary endpoint was safety. The secondary endpoint was efficacy.
Results
105 pts were enrolled (23 cHL, 31 B-NHL, 23 T-NHL, 27 MM and 1 chronic myelogenous leukemia). Pts were heavily pretreated with 88%, 78%, 68% and 66% of pts with cHL, T-NHL, B-NHL and MM, respectively, having received ≥3 prior regimens. Previous ASCT was reported for 75% of pts with cHL, 56% of MM, 13% of B-NHL and 9% of T-NHL. As of 1/8/2015, median duration of follow-up was 62 wks (range: 2 to 106+ wks).
Drug-related adverse events (DrAEs) occurred in 71 (67%) pts. The most common DrAEs occurring in >5% were fatigue (15%), rash (11%), diarrhea, pneumonitis, pruritus (each 9%), pyrexia (8%), thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite (each 7%), hypocalcemia, lipase increased, leukopenia, lymphopenia (each 6%) and nausea (5%). Serious DrAE in ≥5% of pts included pneumonitis (5%).
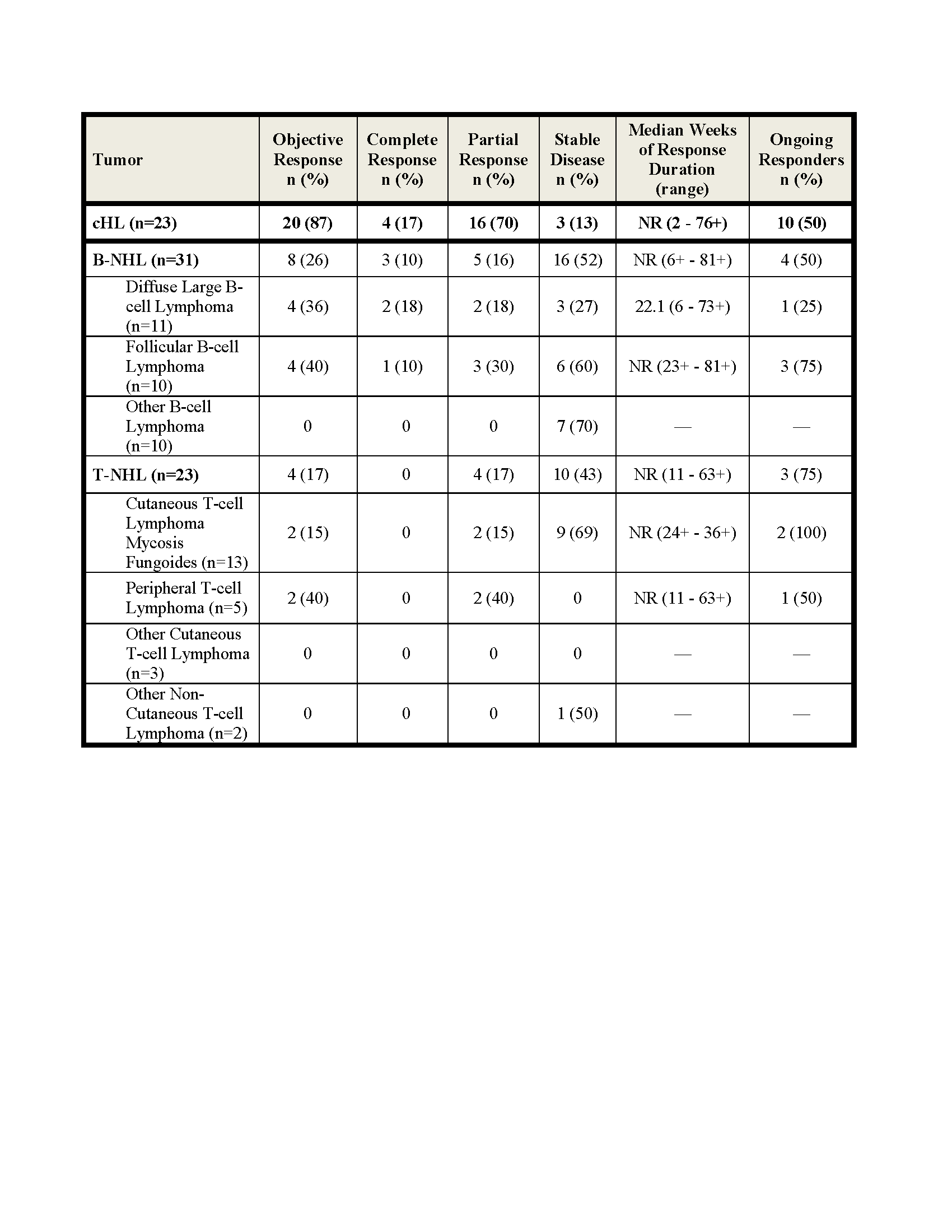
Efficacy results shown below. The rate of stable disease in MM (n=27) was 63%. Among the 20 responding cHL pts, 10 discontinued NIVO; 6 (1CR and 5 PR) to undergo SCT, 3 for disease progression and 1 for toxicity (MDS, thrombocytopenia) and 10 (7 PR and 3 CR) continue to respond. Among responding B- and T-NHL pts, 1/4 DLBCL, 3/4 FL and 3/4 T-NHL pts remain in response. In this updated analysis, median duration of response has not been reached in cHL, B-NHL and T-NHL.
Summary
Encouraging, durable objective responses were observed in cHL, DLBCL and FL, including CR and PR. NIVO treatment remains safe and tolerable with a safety profile similar to that in solid tumors, and further analysis is warranted in cHL and selected B-NHLs and T-NHLs.
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Immunotherapy, Multiple myeloma, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
Session topic: Progess in Hodgkin lymphoma therapy: Incorporation of novel agents and reduction of side effects
Type: Oral Presentation
Presentation during EHA20: From 14.06.2015 08:45 to 14.06.2015 09:00
Location: Room Lehar 3 + 4
Background
The PD-1 pathway functions as a checkpoint which limits T-cell mediated tumor immune responses. Nivolumab (NIVO), a fully human IgG4 monoclonal PD-1 blocking antibody, potentiates T-cell activity. Prior results from this study (median follow-up 40 weeks) showed that NIVO was tolerated and achieved an overall response rate of 87% in classical Hodgkin lymphoma (cHL), 40% in follicular B-cell lymphoma (FBL), 36% in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and 17% in T-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma (T-NHL). The stable disease rate in multiple myeloma (MM) was 67%.
Aims
Herein, we report the updated follow-up and safety profile of this study.
Methods
Patients (Pts) were treated using a dose-escalation design (1 and 3 mg/kg) of NIVO administered every 2 weeks (wks) for 2 years. Responses were assessed using standard criteria. Primary endpoint was safety. The secondary endpoint was efficacy.
Results
105 pts were enrolled (23 cHL, 31 B-NHL, 23 T-NHL, 27 MM and 1 chronic myelogenous leukemia). Pts were heavily pretreated with 88%, 78%, 68% and 66% of pts with cHL, T-NHL, B-NHL and MM, respectively, having received ≥3 prior regimens. Previous ASCT was reported for 75% of pts with cHL, 56% of MM, 13% of B-NHL and 9% of T-NHL. As of 1/8/2015, median duration of follow-up was 62 wks (range: 2 to 106+ wks).
Drug-related adverse events (DrAEs) occurred in 71 (67%) pts. The most common DrAEs occurring in >5% were fatigue (15%), rash (11%), diarrhea, pneumonitis, pruritus (each 9%), pyrexia (8%), thrombocytopenia, decreased appetite (each 7%), hypocalcemia, lipase increased, leukopenia, lymphopenia (each 6%) and nausea (5%). Serious DrAE in ≥5% of pts included pneumonitis (5%).
Efficacy results shown below. The rate of stable disease in MM (n=27) was 63%. Among the 20 responding cHL pts, 10 discontinued NIVO; 6 (1CR and 5 PR) to undergo SCT, 3 for disease progression and 1 for toxicity (MDS, thrombocytopenia) and 10 (7 PR and 3 CR) continue to respond. Among responding B- and T-NHL pts, 1/4 DLBCL, 3/4 FL and 3/4 T-NHL pts remain in response. In this updated analysis, median duration of response has not been reached in cHL, B-NHL and T-NHL.
Summary
Encouraging, durable objective responses were observed in cHL, DLBCL and FL, including CR and PR. NIVO treatment remains safe and tolerable with a safety profile similar to that in solid tumors, and further analysis is warranted in cHL and selected B-NHLs and T-NHLs.
Keyword(s): Hodgkin's lymphoma, Immunotherapy, Multiple myeloma, Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma

Session topic: Progess in Hodgkin lymphoma therapy: Incorporation of novel agents and reduction of side effects